# 链表
# 02. 两数相加 (opens new window)
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
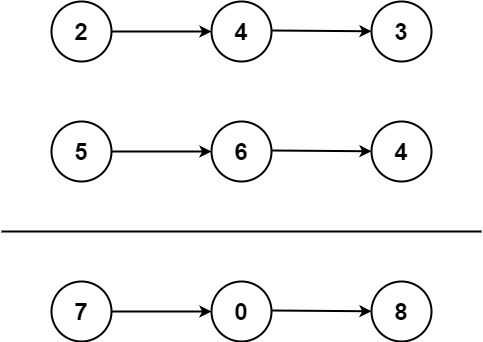
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
2
3
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
2
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
2
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
const res = new ListNode(0);
// node 保留指向
let node = res;
let needAdd = 0;
// 循环条件说明:l1l2可能长度不同 进位可能在l1l2循环结束后还有需要进位的 所以要加上判断
while (l1 || l2 || needAdd) {
// 可能l1l2长度不同
const val1 = l1 ? l1.val : 0;
const val2 = l2 ? l2.val : 0;
// 加上需要进位的数一起求和
const val = val1 + val2 + needAdd;
node.next = new ListNode(val % 10);
// 如果结果大于十还是需要进位 否则归零
needAdd = val >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
node = node.next;
l1 = l1 ? l1.next : l1;
l2 = l2 ? l2.next : l2;
}
return res.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 19. 删除链表的倒数第N个结点 (opens new window)
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
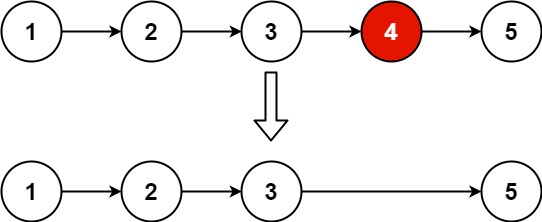
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
2
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
2
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
/**
* 快慢指针
* 1. 搞一个虚拟头节点 指向head(方便删除头结点的情况
* 2. 快指针先走n+1步
* 3. 此时如果已经为null 那么直接删除头(因为题目n必然有效)
* 4. 指针同时一步步走 快指针为null时 慢指针的val就是要删除的
*/
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0,head);
let [slow, fast] = [dummyHead, dummyHead];
// 快指针走n+1
let step = n+1
while(step--){
if(!fast){
// fast如果已经没了 直接去掉头结点
return head.next
}
fast = fast.next
}
while(fast){
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
}
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummyHead.next
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 206. 反转链表 (opens new window)
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
2
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
2
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
2
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function (head) {
let prev = null
while (head) {
// 234
const next = head.next
// 1null
head.next = prev
prev = head
head = next
}
return prev
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 21. 合并两个有序链表 (opens new window)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
2
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
2
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} list1
* @param {ListNode} list2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) {
/**
* 两个指针
* 如果节点值一样 分别填入
* 不一样填入小的 向后一位 直到所有的都结束
* 递归
*/
if(!list1) return list2
if(!list2) return list1
if(list1.val<list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2)
return list1
}else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list2.next,list1)
return list2
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 146. LRU 缓存 (opens new window)
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。 实现 LRUCache 类: LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存 int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。 void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。 函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
题解
题目要求必须0(1) 所以不能用数组 数组的操作基本都是O(n) 由于我们需要反复对节点进行查找删除添加换位置的操作,满足O(1)查找的就是Map,而定位换位的操作,只有双向链表是符合的,单向链表如果要插入到最后需要从头节点遍历是O(n),而map又没有顺序性只能用到查找,双向链表具有前后指针,在删除和插入时只要改变指针就可以操作,不用影响整体
class TwoWayListNode {
public key: number | null
public value: number | null
public pre: TwoWayListNode = null
public next: TwoWayListNode = null
constructor(key?: number, value?: number) {
this.key = key
this.value = value
}
}
class LRUCache {
private count: number = 0
private capacity
private hashMap = new Map<number, TwoWayListNode>() // map用来存放key和node的映射
// 需要虚拟头结点和尾节点作为链接用
// 最近值放到尾部 最远的值放到头部
private dummyHead = new TwoWayListNode()
private dummyTail = new TwoWayListNode()
constructor(capacity: number) {
this.capacity = capacity
// 头尾连接
this.dummyHead.next = this.dummyTail
this.dummyTail.pre = this.dummyHead
}
public get(key: number): number {
// map中有没有值
if (!this.hashMap.has(key)) {
return -1
} else {
// 获取到节点 节点放到链条尾部
const node = this.hashMap.get(key)
this.moveNodeToTail(node)
return node.value
}
}
public put(key: number, value: number): void {
// 如果没有 放入 尾部 判断长度
if (!this.hashMap.has(key)) {
const node = new TwoWayListNode(key, value)
this.addNewNodeToTail(node)
this.hashMap.set(key, node)
if (++this.count > this.capacity) {
this.removeLRUNode()
}
} else {
// 有值改值 放入尾部
const node = this.hashMap.get(key)
node.value = value
this.moveNodeToTail(node)
}
}
private removeLRUNode() {
const lruNode = this.dummyHead.next
this.dummyHead.next = lruNode.next
lruNode.next.pre = this.dummyHead
this.count--
this.hashMap.delete(lruNode.key)
}
private addNewNodeToTail(node: TwoWayListNode): void {
// 转移node到尾部
node.pre = this.dummyTail.pre
node.next = this.dummyTail
this.dummyTail.pre.next = node
this.dummyTail.pre = node
}
private moveNodeToTail(node: TwoWayListNode): void {
// 链接node的前后 把自身移除
node.pre.next = node.next
node.next.pre = node.pre
// 转移node到尾部
node.pre = this.dummyTail.pre
node.next = this.dummyTail
this.dummyTail.pre.next = node
this.dummyTail.pre = node
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new LRUCache(capacity)
* var param_1 = obj.get(key)
* obj.put(key,value)
*/
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
# 234. 回文链表 (opens new window)
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1: 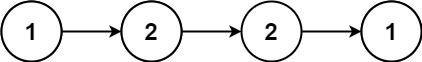
输入:head = [1,2,2,1]
输出:true
2
题解
- 递归法,递归的特点是,可以从底往回,所以适合本题
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
let frontPointer
var isPalindrome = function (head) {
frontPointer = head
return recursivelyCheck(frontPointer)
};
recursivelyCheck = (currentNode) => {
if (currentNode !== null) {
// 递归结果由下到上执行
if (!recursivelyCheck(currentNode.next)) {
return false
}
// currentNode由后向前
if (currentNode.val !== frontPointer.val) {
return false
}
// 递归返回过程中向后移动指针,frontPointer由前向后
frontPointer = frontPointer.next
}
// 递归到最后一层会直接返回true,相等的情况也是true
return true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
- 利用快慢指针找到中点,然后把后半链表翻转比较,
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPalindrome = function (head) {
// 快慢找中间点
let s = head,
f = head;
while (f.next && f.next.next) {
s = s.next;
f = f.next.next;
}
// 偶数s指向中间前一个 奇数指向中间
let mid = s.next;
// 翻转后半链表
let pre = null;
while (mid) {
let temp = mid.next;
mid.next = pre;
pre = mid;
mid = temp
}
// 比较head 和 pre
while (pre) {
if (pre.val !== head.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
